Connect With Authors
*Your message will be sent straight to the team/individual responsible for the article.
In 1901, the British passed legislation allowing the six colonies of Australia to be fully self-governing and formed the Commonwealth of Australia. Since then, Australia and the United Kingdom have gradually alienated, and in 1986, the legislation completely separated from the United Kingdom to become an independent Commonwealth of Australia. However, in terms of constitutional monarchy, Australia still respects the British monarch as its Head of State, similar to India, Canada, and dozens of others.
During World War II, as the United States became the dominant player in the Asia-Pacific region after the war, Australia and the United States increased military exchanges, and the United States also replaced the United Kingdom as Australia’s main military alliance. During the Cold War, intelligence cooperation by the Five Eyes alliance further strengthened this situation. In recent years, with the return of the United States to the Asia-Pacific under the Obama administration, and the establishment of the military-diplomatic-security partnership AUKUS during the Trump administration, exchanges between Australia and the United States have also been greatly strengthened.
In terms of trade, China has been Australia’s largest trading partner since the end of 2000. However, in recent years, there has been a strong deterioration between the two nations citing factors such as military alliance with the US, geopolitical tensions, and a much stronger stance took by the previous Morrison government. This has eventually propelled China to impose trade penalties on Australia through import restrictions and other means. However, due to factors such as China’s domestic demand and the new government (the Labor Party government)’s softening attitude towards China, the relationship between the two parties has gradually warmed up.
While the Labor party, the current governing body, advocate for a stronger role of the state in the economy, they also promote deeper collaborations with the private sector. They plan to prioritize green energy, workplace inclusion, and public-sector reform. In terms of climate change, the government is seeking to overhaul the “safeguard” mechanism that enforces emission-intensity reductions among big polluters by mid-2023. This reform is part of a package of measures designed to reduce emissions to 43% below 2005 levels by 2030 and achieve net-zero emissions by 2050. The government will provide financing for green energy, upgrading the electricity network, and promoting the adoption of electric vehicles to create business opportunities.
Labor intends to reorient the country’s institutions to achieve its vision. The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) may undergo an independent review that could broaden its mandate beyond inflation targeting, while the Productivity Commission may undergo reforms to prioritize productivity over other macro areas. The National Anti-Corruption Commission, which was legislated for in 2022, will begin operations in mid-2023.
18.36 Billion
- %
-2.3 %
50.7 %
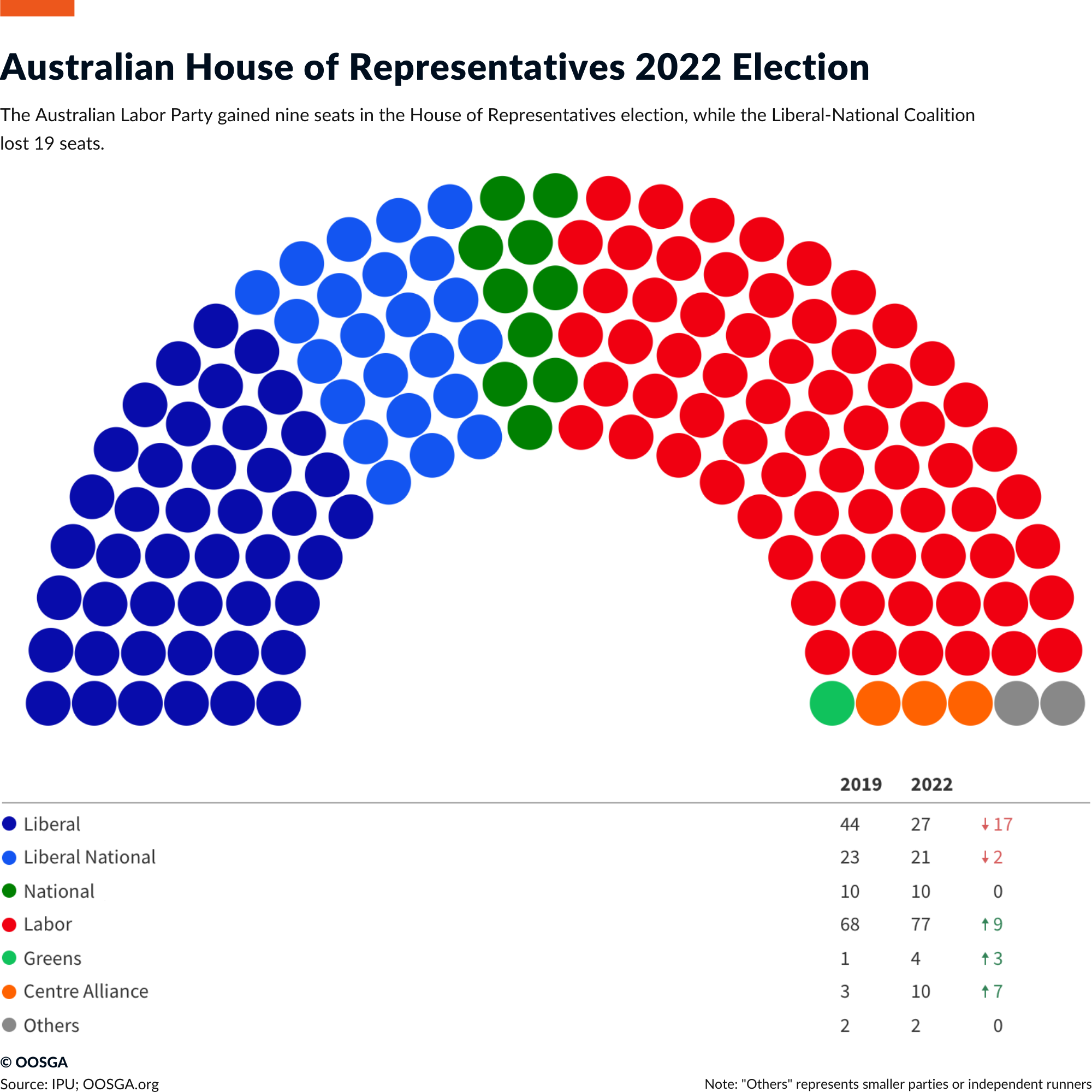
In the May 2022 election, the Labor party won 77 out of the 151 seats in the House of Representatives, which was an increase from 68 in the 2019 election. These gains came at the expense of the Liberal-National coalition, which lost seats and now holds only 58, making it difficult for them to return to power in the next federal election in 2025. The election outcome was not necessarily a strong endorsement of Labor, as their share of the popular vote actually decreased. Instead, it was more of a rejection of the former governing coalition, whose vote share dropped even more.
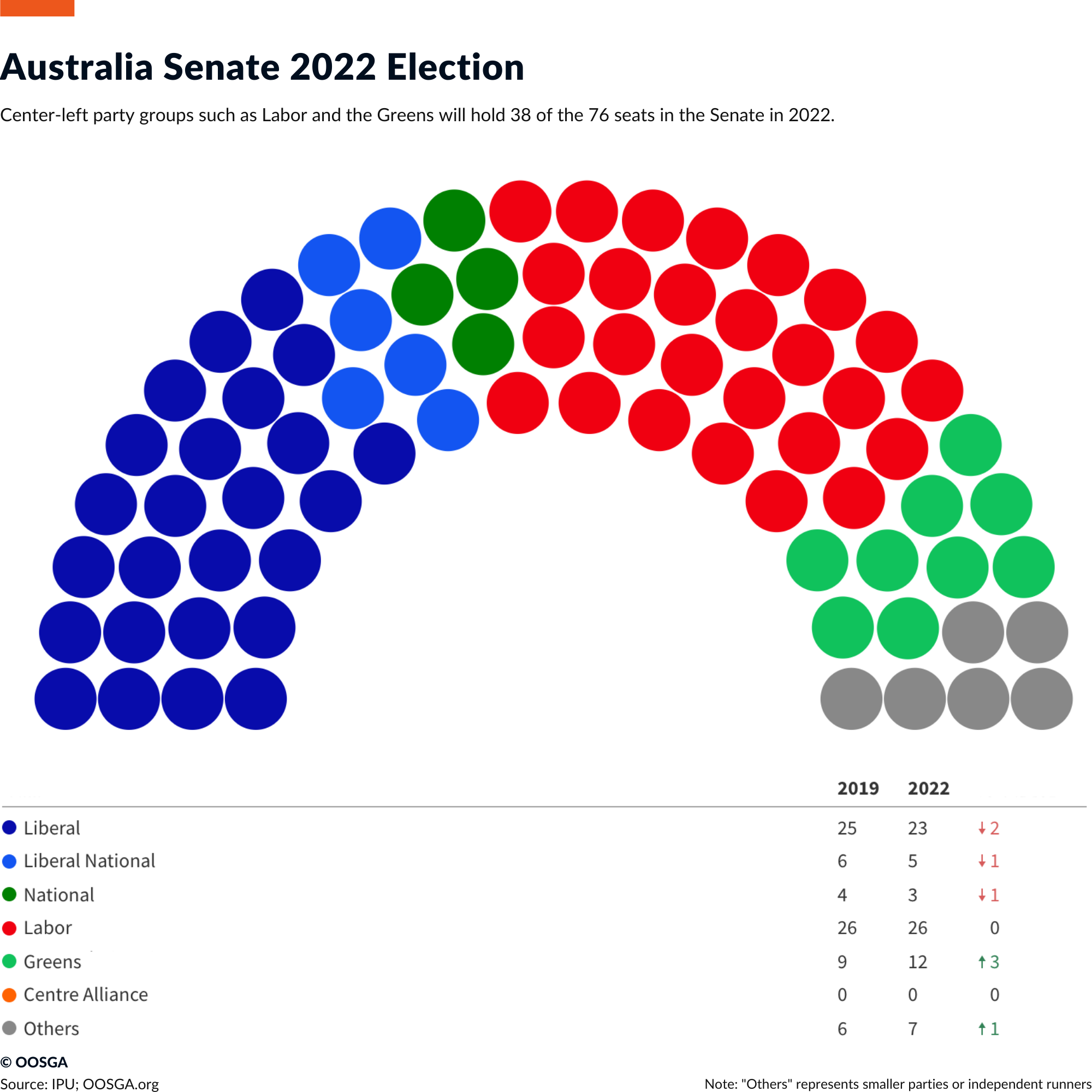
The impact of minor parties and independent politicians on policy will be more significant. The biggest gains in the election were made by crossbench members, with the Greens winning four seats and the number of independent politicians (led by the loosely organized “teal” group) increasing. Labor will seek cooperation with these groups on a case-by-case basis and they will be crucial in getting legislation passed through the Senate, where Labor still only holds a minority of seats.
Labor has promised to hold a referendum on the creation of an Indigenous Voice to Parliament, which would be a permanent and constitutionally recognized Indigenous advisory body to the federal government. According to the government, it is likely that the vote will happen in 2023. Although this will be the primary focus for constitutional matters, the likelihood of a referendum on the establishment of an Australian republic has increased following the death of Queen Elizabeth II. Labor is expected to include it as part of their campaign in the 2025 election, and if they win again, a vote could be held soon after. The leader of Labor, Mr. Albanese, supports the idea of a republic and has appointed an assistant minister for the republic to his cabinet.
-
22
Political stability in Australia is expected to deteriorate as China becomes more assertive in challenging Australia’s dominance in the Pacific and tensions rise between the country’s two main political parties. The macroeconomic environment is also likely to not perform as well as before. Despite the economy’s expected growth, the combination of rapid inflation and rising interest rates will make conditions difficult for both consumers and businesses, and the pandemic has resulted in an increase in public debt. To keep China away from national strategic interests, the country has become less welcoming towards foreign investment and funding has declined due to tighter liquidity.
However, when it comes to the attractiveness of the market, it is getting better than pre-pandemic. The economy has recovered from the 2020 coronavirus recession and is expected to continue growing overall, with both imports and exports predicted to increase in the next five years. The foreign trade and exchange control aspect is expected to strengthen further as Australia expands its free-trade agenda and signs major trade deals with the EU and India.
-
12
Australia’s labor policy is a complex legal framework consisting of legislation, common law, binding awards, and custom and practice. The Fair Work Act 2009 (FWA) established a new national workplace-relations system, standardizing labor relations regulations in the private sector with varied degrees of public-sector implementation. The Workplace Relations Amendment (Transition to Forward with Fairness) Act 2008 and the FWA are the legislative basis of this system, which created 122 modern awards to replace over 2,400 pre-existing industry- and occupation-specific pay and work conditions.
The FWA expanded the scope of pre-existing unfair-dismissal laws, set rules for collective bargaining, established a dispute-resolution process, and created the Fair Work Commission (formerly Fair Work Australia), the federal workplace-relations tribunal. Additionally, it established the National Employment Standards (NES) on pay and work conditions, under which dismissed workers may file unfair-dismissal complaints. However, higher-income employees earning over A$153,600 are excluded from this process unless covered by a modern award.
The NES, effective since 2010, sets employment norms in ten categories, including working hours, flexible work arrangements, annual leave, community-service leave, long-service leave, parental leave, personal and compassionate leave, public holidays, termination and redundancy pay, and the Fair Work Information Statement. These standards apply to full- and part-time employees, while only some apply to casual workers who are employed on an hourly or daily basis and do not receive benefits such as sick leave or paid annual leave but are legally entitled to a higher minimum hourly wage rate.
16.08 $
27.77 $
4110 $
0.0829 %
Australia’s infrastructure development policy focuses on improving connectivity and increasing state and federal government spending on transport and other infrastructure. A key aspect of the successful Labor election manifesto, this policy is championed by Prime Minister Anthony Albanese. Infrastructure Australia, a statutory body, is responsible for specifying national- and state-level priorities, emphasizing the need for resilient road and rail links in regional Australia. To capitalize on demand for agricultural and mineral-resource commodities in Asia, Australia must continue investing in its port and rail networks, with the corporate sector playing a significant role in the entire supply chain.
Two major projects recommended for federal funding are the Australia-Asia Power Link in the Northern Territory (NT) and the redevelopment of Circular Quay in Sydney. The Australia-Asia Power Link project includes the construction of the world’s largest solar farm with large-scale battery storage and a long subsea electricity cable, providing no-emission electricity to NT and exporting solar power to Singapore. On the other hand, the Circular Quay redevelopment project aims to overhaul one of Australia’s most visited sites, enhancing transport facilities and public spaces.
In terms of broadband infrastructure, Australia ranks 77th in the fixed broadband Speedtest Global Index, with a median average download speed significantly lower than the global average. To address the inadequacies in wired telecoms networks, the federal government introduced the National Broadband Network (NBN) initiative. Although the NBN rollout was declared complete in 2020, there is still a mix of different technologies in use across the country. As migration from legacy systems continues, average fixed broadband speeds are expected to increase. Additionally, the growing availability of 5G fixed-wireless home broadband services may offer an alternative to the NBN.