Connect With Authors
*Your message will be sent straight to the team/individual responsible for the article.
South Korea has had a democratic institution in place since around 1990, and its chaotic but relatively peaceful presidential elections and party rotation every five years. In the most recent South Korean presidential election (2022), Yoon Suk Yeol of the National Power Party defeated Lee Jae-myung of the ruling party at the time by 1% of the votes, and successfully completed the party rotation in the middle of the year.
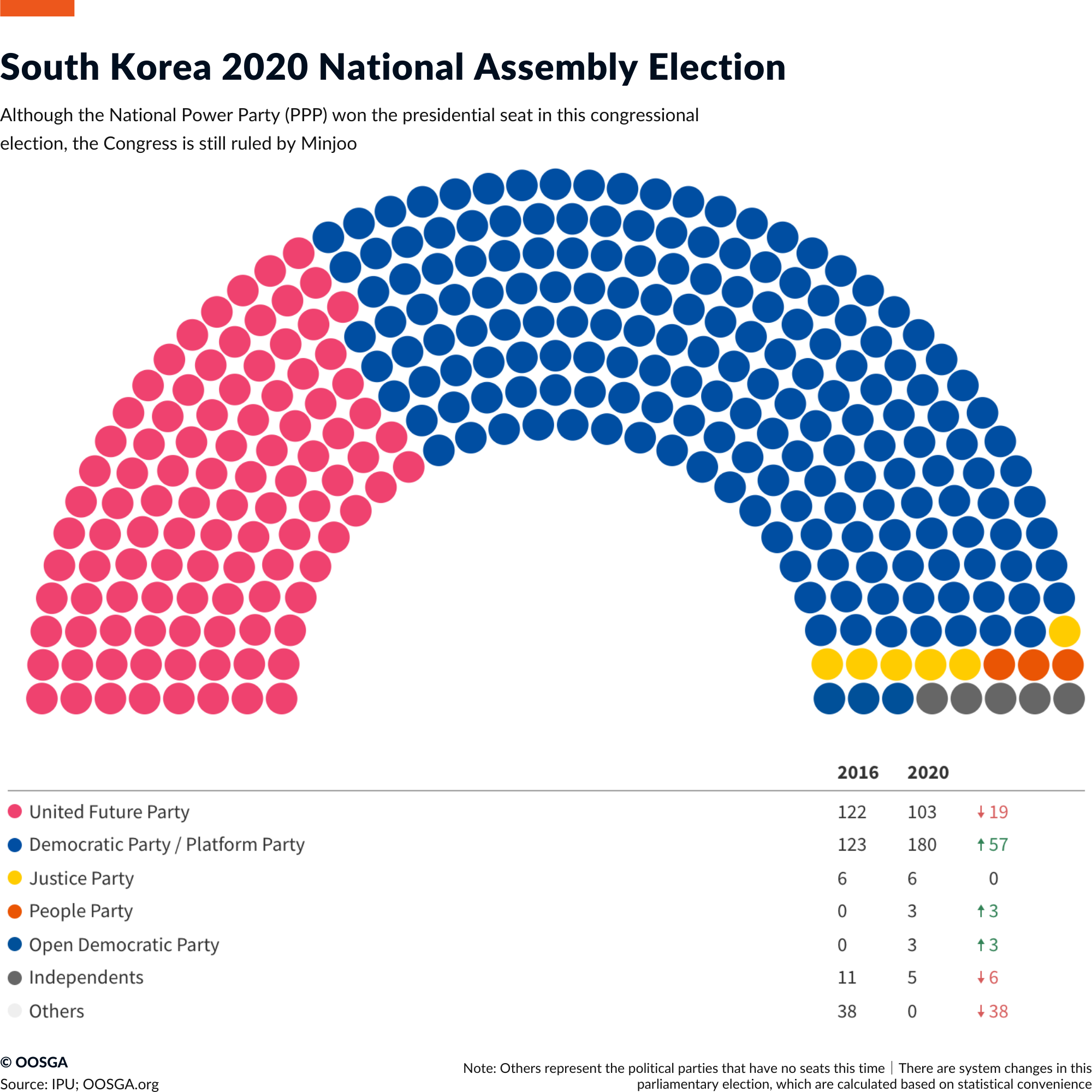
However, in the previous year’s election, due to the overwhelming majority of 180 seats of the Democratic Party, Yoon Suk-yue also faced a big political problem with the North Korean government. At the same time, North Korea also frequently tested missiles due to factors such as South Korea’s increased exchanges with the United States. , also increased the risk of border conflicts; moreover, the outbreak of domestic protests based on people’s livelihood issues (prices) also brought the issue of political stability to the surface.
The current policy focus of the Yoon Suk Yeol government will mainly focus on the deregulation of the labor market and a series of tax cuts to stimulate the mobility of labor, the momentum of investment and employment, and the stability of the economy. At the same time, the Yoon Suk Yeol government is also actively promoting the investment and development of advanced technology and digital infrastructure, hoping that South Korean companies can continue to maintain their leading position in industrial technology for the next ten years.
29.83 Billion
1.8 %
-1.6 %
53.8 %
Yoon Suk-yeol, a former prosecutor and opposition leader, won the South Korean presidential election, defeating Lee Jae-myung of the ruling Democratic Party. Yoon’s victory returns conservatives to power after five years, and his calls for a tougher stance on North Korea and a stronger alliance with the United States are expected to shape South Korea’s future foreign policy. The election was close and was seen as a referendum on President Moon’s progressive administration, which focused on seeking peace and dialogue with North Korea.
Yoon rose to prominence as an anti-corruption crusader and was recruited by the People Power Party to revive the conservative movement. His victory could potentially disrupt President Moon’s progressive agenda, and his government’s focus will be on deregulation of the labor market and tax cuts to stimulate the economy. Yoon is also actively promoting investment and development in advanced technology and digital infrastructure, hoping to maintain South Korea’s leading position in industrial technology. The election outcome will have significant implications for South Korea’s relationships with the United States, China, and Japan.
-
9
The business environment in South Korea is characterized by its strong technological readiness, which is supported by an advanced digital infrastructure, high penetration of mobile electronic devices, and favorable policies and operational conditions for fintech and e-commerce businesses. The country’s agile and resilient external sector will also support the economy during the forecast period. South Korea has a comprehensive industry portfolio and holds a significant share of the global market for electronics and components, particularly memory chips and high-quality panels. This, combined with strong external sector performance, will drive employment and business investment domestically. Additionally, the country’s financial sector is expected to become more global and sophisticated, with the continued growth of fintech.
The South Korean government is supportive of businesses and has implemented policies to promote labor mobility and investment in research and development, as well as trade liberalization and supply chain diversification and resilience. However, the effectiveness of these policies may be limited by confrontational party politics and conflicting policy priorities between the government and an opposition-controlled parliament.
-
5
9.61 $
25.68 $
2930 $
2.051 %