Connect With Authors
*Your message will be sent straight to the team/individual responsible for the article.
Mexico was ruled by the Partido Revolucionario Institucional (PRI) from 1929 to 2000, moving from a nationalist and interventionist approach to a free-market and economically liberal approach. In 2000, the centre-right Partido Acción Nacional (PAN) won the presidency, representing a shift to democratic pluralism, but a divided legislature and slow progress in structural reforms hampered political effectiveness. Sluggish growth and rising violent crime led to the PRI’s return to power in 2012. However, persistent domestic discontent resulted in a historic election win for the left-wing Andrés Manuel López Obrador in 2018.
The Mexican political system is presidential, bicameral, and federal, consisting of 31 states and a federal entity covering the capital city, Mexico City. Presidential terms are for six years with no possibility of re-election. During the transition to democratic pluralism, political power has shifted from the executive to the legislature and local governments. Reforms in 2013 allowed for the re-election of legislators and mayors, and established a single electoral institute to improve political effectiveness and reduce election irregularities. In 2018, presidential candidates were allowed to run as independents, but their impact was limited. López Obrador has a tendency to put major policy decisions to public consultations outside of legal channels.
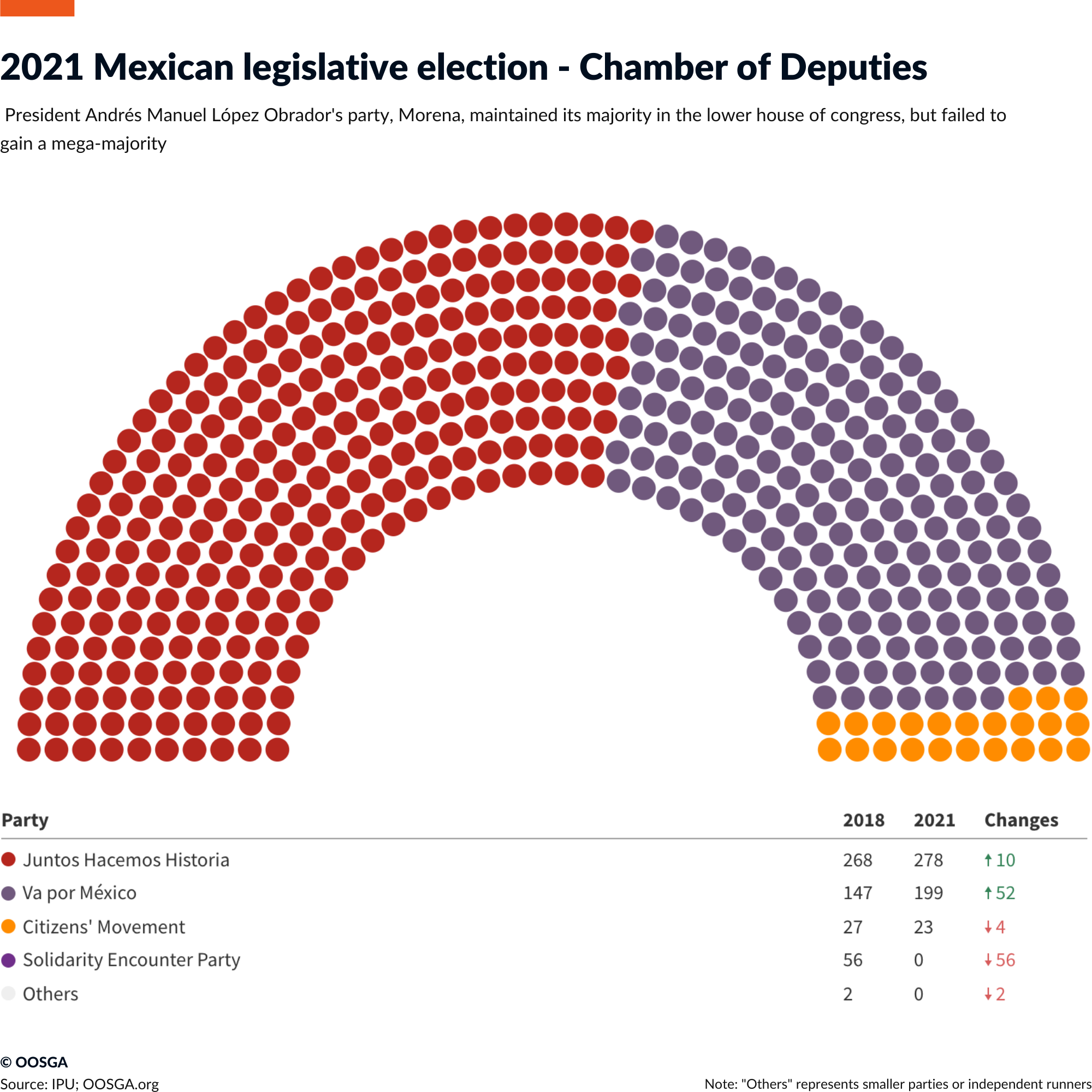
Conservative fiscal and monetary policies support macroeconomic stability, but weak non-oil revenue and shallow credit markets limit policymakers’ ability to boost demand. Previous governments implemented structural reforms in 2013 in energy, education, and telecommunications. López Obrador reversed the education reform by eliminating teachers’ evaluations and attempted to undermine the energy reform, but the loss of a congressional supermajority in the June 2021 mid-term elections limited his efforts. Growth is hindered by a lack of internal competition, a deficient education system, institutional flaws fostering corruption, and high crime levels.
-18.05 Billion
-1.2 %
-4.3 %
54.1 %
Mexican President Andrés Manuel López Obrador’s party, Morena, kept its majority in the lower house of congress with the support of a controversial ally in the midterm elections. Though the party failed to win two-thirds of the lower house, which would have allowed López Obrador to roll back reforms, he still retains institutional power in the budget process and congress. Despite criticism for his handling of the economy, security, and the pandemic, López Obrador still enjoys approval ratings around 60% and is supported for programs such as cash payments for seniors and students, and raising the minimum wage. Despite the setback in Mexico City, Morena performed strongly in state-level races and was leading in 10 of the 15 gubernatorial races.
The near-term political focus in Mexico will be on the state elections in Estado de México and Coahuila on June 4th. These elections are expected to be highly competitive and could provide insight into the political momentum ahead of the presidential and legislative elections in 2024. The ruling party, Morena, remains the favorite to win the presidential race, with several potential candidates including Claudia Sheinbaum and Marcelo Ebrard. On the other hand, the opposition is fragmented with no clear front-runner. The opposition candidate will face the challenge of unifying diverse parties, mobilizing voters, and countering Morena’s incumbency advantage.
-
17
-
41
1.24 $
4.68 $
522 $
1.2793 %