Connect With Authors
*Your message will be sent straight to the team/individual responsible for the article.
With the occurrence of the Siamese Revolution of 1932, Thailand successfully ended 800 years of monarchy rule and opened up a constitutional monarchy era. The military and civilians who led the revolution also established the first people-led political party (Thai People’s Party). However, the party quickly fell apart due to political and interest conflicts. The political environment and democracy in Thailand have continuously experienced political turbulence since its founding and have experienced 19 coups so far.
The most recent one took place in 2014 when the elected Prime Minister, Yingluck Shinawatra, was declared ineligible by the Constitutional Court controlled by the military due to unconstitutional conduct. The military government continued to rule Thailand until 2019, until the former leader of the peace and order committee, Prayut Chan-o-cha, won the support of the military-backed party in the 2019 parliamentary election and was appointed as Prime Minister by the Senate. He then announced the end of the military government.
Although Thailand’s current political environment has returned to the so-called democratic system and process, its systematic design still allows the military to have a significant influence on politics. The For Thai Party, led by the former Prime Minister Thaksin Shinawatra, who was ousted in the 2006 coup, although they won a majority in the House of Representatives in this election and the pro-democracy Future Forward Party also won a high number of seats, the Senate’s 250 seats were all appointed by the military, making constitutional amendment unrealistic for the next decade or so.
In the current international and Thai economic, population, and political situation, Thailand’s policies will focus on several key areas. The most important is based on the intensifying regional competition, Thailand is promoting its development to improve its infrastructure and business, with the Thai 4.0 policy being the most indicative. The Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC) development plan in the policy focuses on airport, port, logistics infrastructure, and communication infrastructure, among others.
-14.71 Billion
- %
-4.6 %
60.5 %
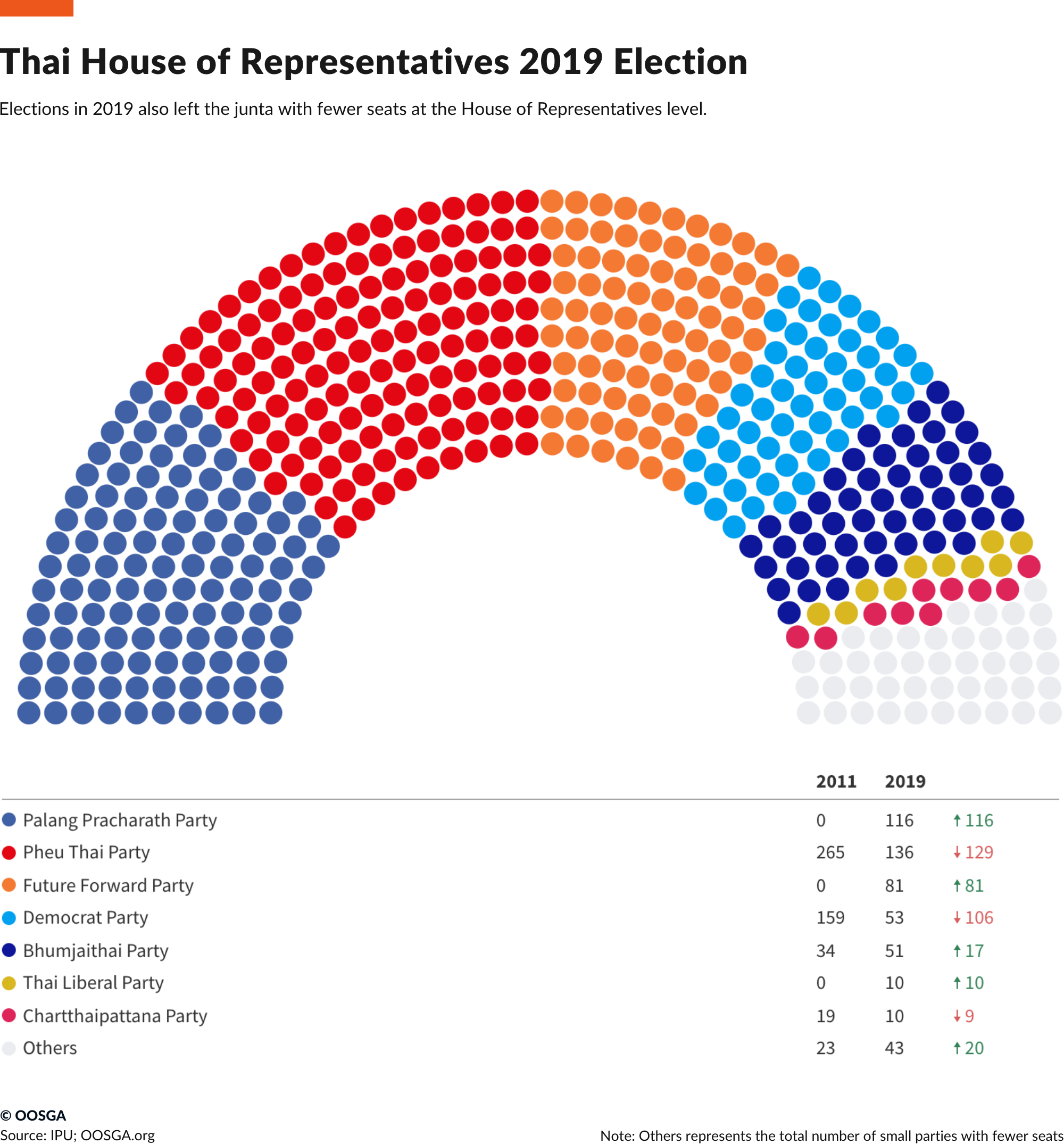
Thailand’s Election Commission announced the final results of the March 24 general election which gave no party an absolute majority and is likely to prompt legal challenges. The commission distributed 150 party list seats in the 500-member House of Representatives under a complicated formula related to each party’s nationwide popular vote total. The Pheu Thai party associated with former Prime Minister Thaksin Shinawatra received none of the party list seats and has issued a statement saying the Election Commission “deliberately intended to commit wrongdoing and misused its power, violating the constitution and the law.”
Neither party received a majority, and both are attempting to form coalitions with smaller parties to form a government. Prayut Chan-o-cha, who staged the 2014 military coup and has served as prime minister, is the Palang Pracharath party’s candidate to continue in that role. Prayut is expected to easily return to office as the prime minister will be selected by a joint vote of the lower house and the appointed Senate, however, he will have a hard time if his foes control the lower house. The Future Forward Party, which shares Pheu Thai’s anti-military stance, has agreed to join it in a coalition.
The next general election in Thailand is scheduled for May 2023, with the exact date expected to be announced in early March. The opposition is expected to make significant gains, with Paetongtarn leading in recent opinion polls for the prime minister position. The opposition party, PTP, will need an overwhelming victory or an alliance with other opposition parties to secure a simple majority in the lower house. The royalist-military alliance is expected to maintain its strong influence in Thai politics in the 2023-2027 period.
-
25
The business environment in Thailand is expected to improve in the near term due to the normalization of domestic economic conditions after lifting coronavirus restrictions. Area such as technology development and the market opportunities have improved the most over the past few years.
The improvement in infrastructure and policy towards foreign investment will encourage a moderate rise in investment. The “Thailand 4.0” initiative will proceed but will face growing challenges due to tighter fiscal space after the pandemic.
The Bank of Thailand (BOT) will continue to raise policy rates gradually in 2023. The central bank will remain independent, and its governor will have to balance between reviving the economy and curbing inflation, which will result in a gradual but longer monetary tightening cycle compared to its peers and the US.
Rapid inflation and high household debt will continue to weigh on private consumption prospects, while lackluster domestic demand will remain a drag on business sentiment. The country’s global and regional ranking will remain unchanged during the forecast period.
-
17
1.29 $
1.8 $
415 $
2.1091 %