Connect With Authors
*Your message will be sent straight to the team/individual responsible for the article.
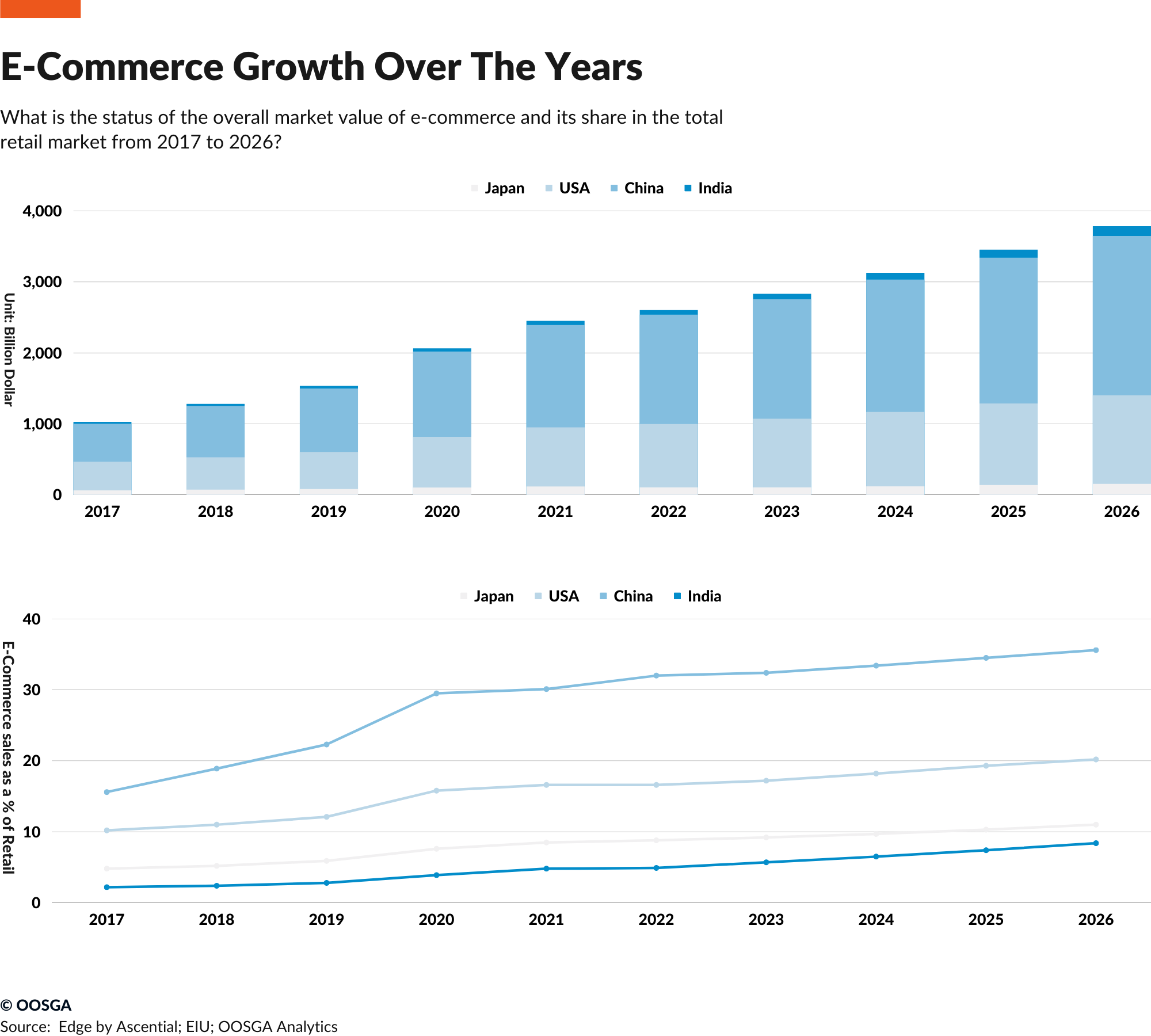
The pandemic has changed how we consume, and in turn, it’s altered our spending habits. This is why there was a significant increase in the share of ecommerce in total retail during 2019-2020. Studies also found that new ways and habits developed during the pandemic, such as online shopping, food delivery platforms, remote work, and others are expected to continue.
While these numbers and trends seem to paint a bright future for ecommerce, among millions of ecommerce websites globally
At the same time, while many ecommerce platforms currently support domestic consumption or help numerous Greater China businesses implement cross-border ecommerce, this often means intense price wars and difficulty in establishing deeper relationships with customers for many operators.
Therefore, we have compiled some ecommerce trends and resources from different countries to support our clients in implementing ecommerce strategies, thus supporting sustainable and healthy growth.
Electronic Commerce, commonly referred to as ecommerce, refers to all business activities carried out via the internet. These activities include product selection, transactions, logistics to deliver goods to consumers, and after-sales service.
Compared to traditional retail, which requires substantial initial investment and maintenance costs, the initial investment for ecommerce is relatively less and more affordable for small and medium-sized businesses.
We can further categorize ecommerce into two types of targets and two operating models, which are the primary methods many businesses use to evaluate the market.
This type of ecommerce is what most consumers use daily. Examples of self-operated B2C include PX Mart PXGo, Nike online store, Uniqlo online store, and more.
For small businesses with less resources, the initial investment for self-operated ecommerce is usually higher, and they face technical challenges in many areas, such as IT infrastructure, payment systems, and traffic generation.
As a result, many businesses prefer semi-self-operated solutions, where third-party operators handle IT, payments, and even logistics, while the business retains full flexibility in other aspects.
Non-self-operated ecommerce belongs to third-party platform ecommerce, with Amazon, momo, Shopee, Taobao, etc., being the most common ecommerce platforms. In recent years, third-party platforms have added other types of players, such as delivery service providers like Uber, Food Panda, which are increasingly becoming mediums for businesses through online consumption.
Moreover, the rise of social commerce, initiated by Chinese social media in recent years, has started to bloom everywhere. Many platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, and even YouTube have launched social commerce features, enabling businesses to interact with customers in completely new ways.
For self-operated businesses, the B2B ecommerce model was mainly based on re-purchase transactions. However, when the pandemic limited this type of procurement method in early 2020, many companies were forced to look for new buyers or even place orders online.
This trend has led to rapid growth in B2B ecommerce. In a survey by McKinsey, it was found that 32% of businesses stated that ecommerce is the most effective sales method, surpassing physical contact at 23%.
However, B2B ecommerce is still immature in the self-operated aspect. Whether in terms of product and service listing completeness, design, or overall process, there is a huge gap compared to B2C.
Thus, for businesses that do not have ample resources to invest in establishing a complete ecommerce system and funding its operation, many semi-self-operated solutions are a viable option.
In B2B ecommerce platforms, they can typically be further classified into cross-border trade platforms like Alibaba, Taiwan Trade, and industry-specific platforms that support various needs within the same industry.
With advancements in technology, changes in consumer habits, reduction in international trade barriers, and the maturity of various platforms and channels, it is very likely that e-commerce will appear in our lives in a completely different form in just a short span of 10 years. The main aspects include:
Focus on last-mile solutions like 3PL (third-party logistics), delivery platforms, real-time demand forecasting, and drones have been thriving in recent years. Technologies such as third-party logistics and delivery platforms have gradually entered different product categories and are increasingly used by consumers.
Demand forecasting (and real-time supply) is gradually being tested by large enterprises. For example, Amazon, which applied for the Anticipatory Shipping patent in 2014, has started to use it during peak holiday periods.
In the drone field, land drones have already appeared in many cities, and many startups are thriving in this field. Despite many challenges such as regulatory norms, fault tolerance, and many tests and optimization processes, drone delivery (Air & Road) will inevitably enter e-commerce operations and consumers’ lives.
Many technologies surrounding the consumer experience on e-commerce have been thriving in recent years. For example, the 2.5D website experience allows consumers to understand products in a more intuitive way. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) that have been discussed by many businesses in recent years provide a more immersive experience.
Brands like Gucci, Louis Vuitton, and Coca-Cola are actively providing new experiences in the metaverse, while H&M has integrated payment features to provide a complete Metaverse e-commerce experience.
With the further maturity of virtual reality technology, the development and usability of third-party metaverse platforms, infrastructure, devices, and consumer usage popularization, the potential of the metaverse is immense and is very likely to change the face of e-commerce.
Many experience technologies focused on various fields continue to develop. For example, many cosmetic brands have incorporated virtual makeup technology, allowing consumers to try products without going to physical stores. Similar applications also occur in clothing, jewelry, etc.
Today’s online consumption generally occurs on e-commerce websites or apps, whether self-operated or third-party platforms. However, the vast majority of consumers usually only go to e-commerce websites when they have a purchase intention, and most of the online time is spent on social media, games, and other media.
As consumers used to see advertisements on Instagram or Facebook and click to enter the brand e-commerce website to make purchases, social platforms are now actively promoting consumers to complete purchases on the platform itself. It integrates various existing services of social platforms, allowing users to consume more intuitively (and also more easily) on social platforms.
Although social commerce is popular in the Chinese market, its development in other countries is also gradually accelerating. For example, Bain Consulting pointed out that social commerce in the Indian market will grow at a rate of 50-60% (CAGR) during FY2020-2025.
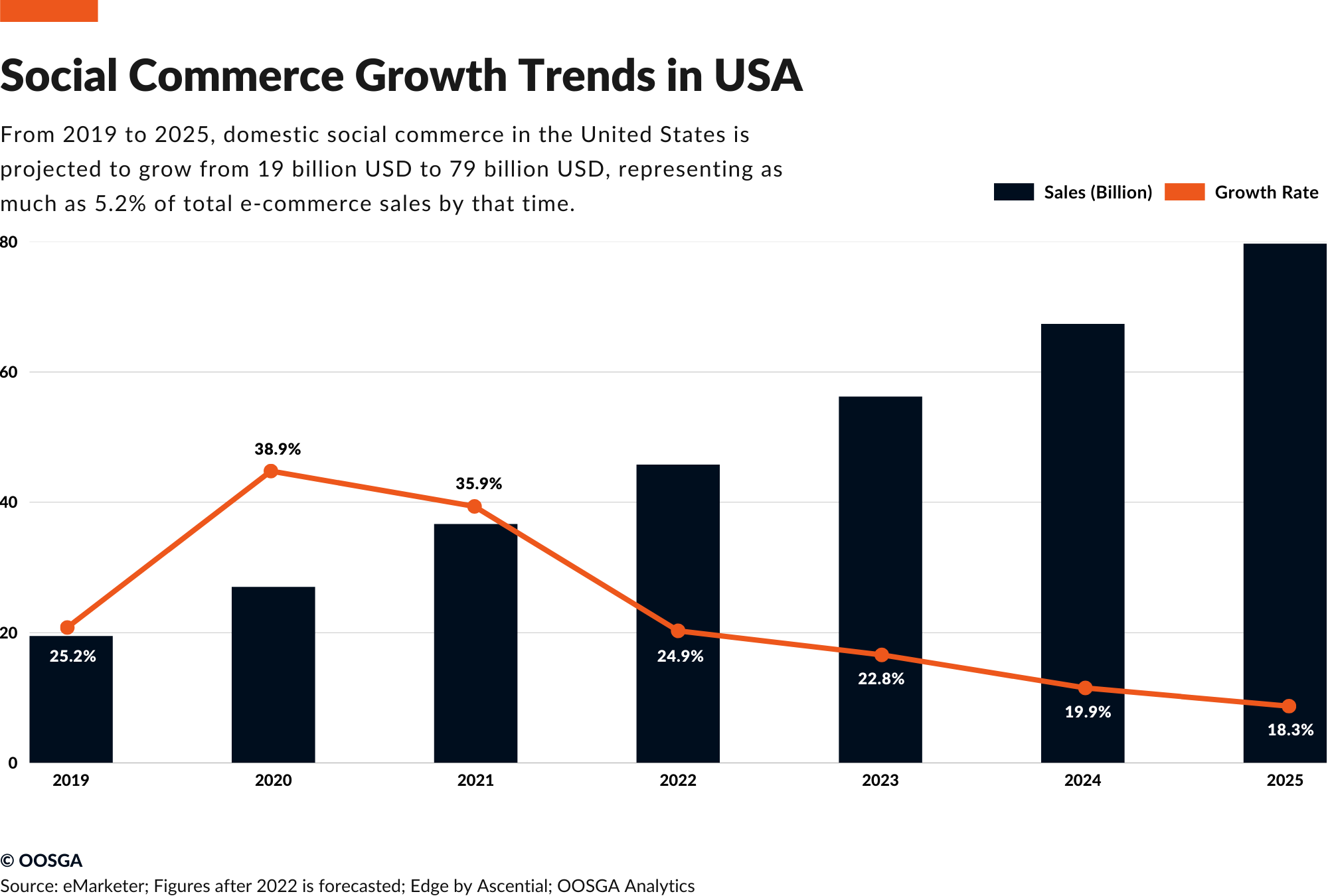
In the United States, the world’s largest terminal market, social commerce is gradually entering consumers’ lives.
However, such developments are not limited to social platforms. As we said before, consumers’ time is not only spent on e-commerce but also on social media, games, and other apps and websites.
A study by Deloitte pointed out that as many as 36% of consumers are very eager to purchase customized products, and one in five consumers is willing to pay an extra 20% for personalized products. With the robust development of technologies such as additive manufacturing, the Internet of Things, and industrial automation that support mass customization, e-commerce is going to completely change its face.
For consumer goods, many companies like Nike, Apple, etc., already provide personalized services for their products on e-commerce websites. In the future, with the reduction in cost, companies will further provide deeper personalization, such as scanning consumer’s feet through an App, and making a pair of shoes that best fit their size and shape based on the data.
In packaged foods, especially those that prioritize health, more and more companies are investing in developing foods that are completely customized to the consumer’s physical condition. With the prevalence of health data sharing, further maturation of automation technology, and more research and testing of personalized diets, this trend will change the face of food e-commerce.
The application of the subscription-based consumption model in the e-commerce field is not a new concept. Ordering magazines through the internet or the Dollar Shave Club began to implement corresponding measures very early and achieved great success. However, even more than a decade later, we hardly subscribe for goods that consumers generally buy regularly and in fixed quantities, like toilet paper. The main reason behind this is that consumers lack sufficient motivation to adopt subscriptions. This is due to the prevalence of retail, the convenience provided by e-commerce itself, and many consumers enjoying so-called freedom of choice.
But this situation is changing. With the continuous development of product personalization, membership systems, and the integration of brands and consumer life, subscriptions will become a norm in many consumer goods categories.
The combination of brands with more consumer life, as mentioned before, is very obvious in the Internet of Things. For example, HP Instant Ink’s ink subscription is a benchmark case in the industry that combines IoT and subscription.
Like ink, many consumables, when combined with IoT applications and direct ordering through mobile apps, can support consumers to have a better usage and after-sales experience.
With the threshold of AI applications getting lower and lower, coupled with the maturity of artificial intelligence technology at all levels of e-commerce. Such as back-end supply-demand matching, warehouse automation, inventory management, optimal logistics route determination, supply chain management, and demand forecasting; as well as front-end AI-based product recommendation mechanisms, pricing, chatbots, personalized marketing, personalized experience, and analysis of customer journeys to mine insights, etc.
The application of AI technology in the field of e-commerce is not only optimizing the existing foundation but also changing the entire operation model of e-commerce, enabling the development of new business models.
We track the e-commerce development of various countries, including their online penetration, platform development, and local retail trends.
Our CR team is dedicated to keeping a pulse on the ever-evolving demographics and behavior of consumers globally. We stay informed on the latest trends and developments across major economies to ensure that we are providing the most up-to-date insights for our clients